- 2021-10-12 发布 |
- 37.5 KB |
- 65页


申明敬告: 本站不保证该用户上传的文档完整性,不预览、不比对内容而直接下载产生的反悔问题本站不予受理。
文档介绍
中考英语复习(语法专项案)十三 句子的种类
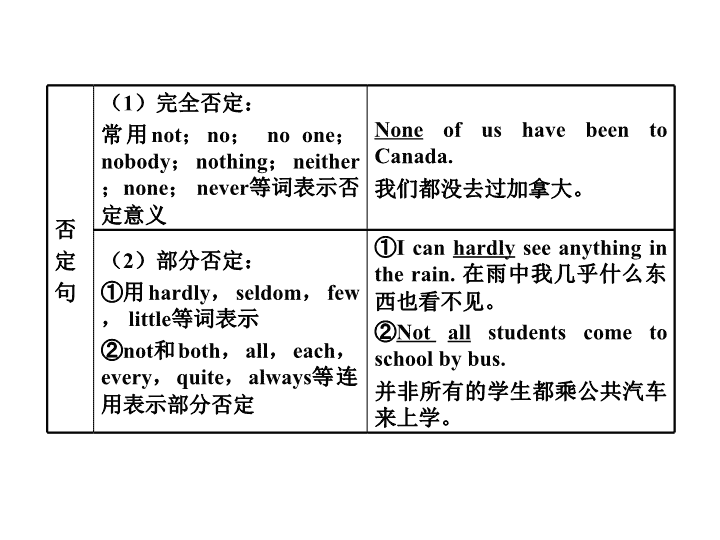
十三、句子的种类 考点一 陈述句和疑问句 一、陈述句 用来陈述一件事实或表达说话者看法的句子叫作陈述句,句末用句号表示句子的陈述结束。陈述句分为肯定句和否定句。 肯定 句 肯定句的基本结构是“主语 + 谓语” I play basketball after school. 我放学后打篮球。 否 定 句 ( 1 )完全否定: 常用 not ; no ; no one ; nobody ; nothing ; neither ; none ; never 等词表示否定意义 None of us have been to Canada. 我们都没去过加拿大。 ( 2 )部分否定: ①用 hardly , seldom , few , little 等词表示 ② not 和 both , all , each , every , quite , always 等连用表示部分否定 ①I can hardly see anything in the rain. 在雨中我几乎什么东西也看不见。 ② Not all students come to school by bus. 并非所有的学生都乘公共汽车来上学。 二、疑问句 用来表示提问的句子叫作疑问句,句末用问号。疑问句包括一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句四种。 (一)一般疑问句 用法 例句 (1) 以系动词 be 开头的疑问句 Are you a student? 你是学生吗? (2) 以助动词开头的疑问句 Do you speak French? 你说法语吗? (3) 以情态动词开头的疑问句 Can you dance? 你会跳舞吗? (二)特殊疑问句 用特殊疑问词引导的疑问句叫作特殊疑问句。特殊疑问词包括疑问代词、疑问副词和由疑问词构成的疑问短语。 引导词 用法 例句 常用疑 问代词 what 什么; who 谁; whom 谁( who 的宾格); which 哪个(些); whose 谁的;疑问代词可以提问主语、谓语、表语或定语 What are you doing? 你在干什么? 引导词 用法 例句 常用疑 问副词 when 何时; where 何地; how 怎么; why 为什么 Where are you going tomorrow? 明天你去哪儿? 常用疑 问短语 what time 什么时刻; how many/much 多少; how often 多久一次; how soon 多久; how long 多长时间; how far 多远; how old 多大(年龄); how big 多大 — How long have you been here? —— 你来这儿多久了? —For 10 minutes. —— 十分钟了。 (三)选择疑问句 用来在两种或两种以上情况中进行选择的疑问句叫作选择疑问句。答语不能用 Yes/ No 回答,而应从问句中选择一种情况进行回答。 用法 例句 一般选择疑问句的构成:一般疑问句 +or+ 被选择的内容 Are you a teacher or a doctor? 你是一名老师还是一名医生? 特殊选择疑问句的构成:特殊疑问句 +A or B? Which do you like better, tea or coffee? 茶和咖啡你更喜欢哪一个? (四)反意疑问句 附在陈述句后对陈述内容进行反问的句子叫作反意疑问句,也叫附加疑问句。反意疑问句前一部分是陈述句,后一部分是简短问句。陈述部分用逗号结尾,反问部分用问号结尾。例如: It’s a nice day, isn’t it ? 天气不错,不是吗? 1. 基本结构:前肯后否;前否后肯。例如: ① We have talked about it, haven’t we ? 我们已经谈过这件事了,不是吗? ② Mr. Smith isn’t at home, is he ? 史密斯先生不在家,是吗? 【 温馨提示 】 用法 例句 (1) 疑问部分的主语必须与陈述部分的主语一致;当陈述部分的主语是名词或代词时,疑问部分要用相应的人称代词 Mr. Black comes from the UK, doesn’t he ? 布莱克先生来自英国,不是吗? (2) 疑问部分要与陈述部分的时态保持一致 Tom went to the cinema yesterday, didn’t he ? 汤姆昨天去看电影了,不是吗? (3) 答语是肯定的用 “ Yes”; 答语是否定的用 “ No” 。前否后肯的反意疑问句 yes 译为“不”, no 译为“是的” —Ann didn’t come to school last week, did she ? —— 安上周没来上学,对吗? —No, she didn’t. She was ill. —— 是的,她没来。她生病了。 2. 特殊形式 用法 例句 (1) 陈述句是 I am. . . ,反意疑问句用 aren’t I I’m your best friend, aren’t I ? 我是你最好的朋友,不是吗? (2) 当陈述部分是 there be 结构时,反意疑问句部分用 there There are many birds in the tree, aren’t there ? 树上有许多鸟,不是吗? (3) 当陈述部分的主语是指示代词 this , that 时,反意疑问句部分的主语用 it ;主语是 these 或 those 时,反意疑问句部分的主语用 they ①This is an English car, isn’t it ? 这是一辆英国汽车,不是吗? ② These are Russian planes, aren’t they ? 这些是俄罗斯飞机,不是吗? 用法 例句 (4) 当陈述部分含有 never/ nothing/none/no one/seldom/ hardly/ few/little 等否定副词时,反意疑问句用肯定形式 She has never been abroad, has she ? 她从来没有出过国,对吗? (5) 如果陈述部分含有由否定前缀 im- , dis- , un- 等构成的否定意义的词,则陈述部分作肯定处理,反意疑问句仍用否定形式 Mary is unhappy, isn’t she ? 玛丽不高兴,是吗? (6) 陈述句主语是不定代词 something/anything/everything/nothing 等时,反意疑问句中代词用 it Nothing is wrong with the computer, is it ? 计算机没什么问题,是不是? 用法 例句 (7) 陈述句主语为 somebody/ someone/anybody/anyone/everybody/everyone 等时,反问句中代词用 they 或 he ,注意问句动词的数应与 they/ he 保持一致 Everyone has known the news, hasn’t he? / haven’t they ? 大家都知道这个消息了,是不是? 用法 例句 (8) 祈使句的反意疑问句 ①祈使句是肯定形式,其反意疑问句用 will you 或 won’t you 皆可。 ②祈使句是否定形式,其反意疑问句通常只用 will you 构成。 ③以 Let 开头的祈使句构成 反意疑问句时, Let’s 用 shall we 构成反意疑问句, 其他均用 will you 。 ①Be sure to write to us, will/won’t you ? 一定要给我们写信,好吗? ② Don’t smoke in the meeting room, will you ? 请不要在会议室抽烟,好吗? ③ Let’s take a walk after supper, shall we ? 晚饭后我们去散步,好吗? ④ Let the boy go first, will you ? 让那男孩先走,好吗? 【 温馨提示 】 陈述句是 I think/I suppose/I believe/I consider 等结构时,问句一般与从句保持一致。注意“否定前移”。 ① I think you can do it better next time, can’t you ? 我觉得你下次可以做得更好,是不是? ② I don’t believe there will be robots at people’s homes, will there ? 我相信人们的家里不会有机器人的,会有吗? 考点二 感叹句 类别 结构 例句 以 what 引导 What + a/an+ adj . + 单数可数名词 + 主语 + 谓语! What a beautiful mountain it is! 多么美丽的山啊! What+ adj . + 复数可数名词 + 主语 + 谓语! What great inventions he has made! 他的发明多么伟大啊! What+ adj . + 不可数名词 + 主语 + 谓语! What bad weather it is today! 今天的天气多么糟糕啊! 以 how 引导 How+ adj . +a/an+ 可数名词单数 + 主语 + 谓语! How clever a boy he is! 多么聪明的男孩! How+ adj . / adv . + 主语 + 谓语! How quickly Tom runs! 汤姆跑得真快! 【 巧学妙记 】 感叹句,并不难, what 或 how 摆在前。 强调名词用 what ,其余 how 很简单。 名词若是可数单,前带冠词 a 或 an 。 主语谓语放在后,省略也是很常见。 考点三 祈使句 祈使句表达说话人对对方的劝告、叮嘱、建议、请求或命令等。主语 you 通常省略,谓语动词用原形,句末用感叹号或句号。表达请求或劝告时,祈使句句末或句首可以加上 please 表示委婉的语气。 一、肯定祈使句的表现形式 Do 型 动词原形( + 宾语) + 其他成分 Please have a seat. 请坐。 Be 型 Be+ 表语(名词或形容词) + 其他成分 Be quiet! 安静! Let 型 Let+ 宾语 + 动词原形 + 其他成分 Let me help you. 让我帮助你。 二、否定祈使句的表现形式 (1)Do 型和 Be 型的否定式都是在句首加 don’t 构成。例如 : ① Don’t forget me! 不要忘记我! ② Don’t be late for school! 上学不要迟到! (2)Let 型的否定式有两种:“ Don’t +let+ 宾语 + 动词原形 + 其他成分”和“ Let+ 宾语 +not+ 动词原形 + 其他成分”。例如: Don’t let him go. /Let him not go. 别让他走。 (3) 有些可用 no 开头,用来表示禁止性的祈使句。例如: No smoking! 禁止吸烟! 考点四 倒装句 英语句子一般主语在前,谓语在后。但有时因为语法结构的要求或为了表达特殊的强调部分,会把句中的谓语提到主语前面。这种句子叫作倒装句。倒装句的常见句式: 一、 There be 句型 There be 句型表示“存在”,主语在 be 的后面。例如: There is some coffee in the cup. 杯中有些咖啡。 1. there be 与 have 的区别 (1)There be 结构表示“某地有某人 / 物”,强调客观存在。 (2)have(has, had) 表示“(某人)拥有某物”,强调所属关系。例如: Mr. Bush has two daughters. 布什先生有两个女儿。 2. There be 句型的句式变化 (1) 对 There be 句型中的主语提问用: What’s + 地点状语 / 时间状语 ? 例如: There are many birds in the forests. 树林里有许多鸟。 → What’s in the forests? 树林里有什么? (2) 对 There be 句式中数量的提问 ① How many + 可数名词 + are there + 地点状语 ? ②How much + 不可数名词 + is there + 地点状语 ? (3)There be 句型中,反意疑问句的附加部分应用 there 。例如: There’s no air on the moon, is there? 月球上没有空气,是吗? 二、 So+ 助动词 / 系动词 / 情态动词 + 主语 表示与上文中所述肯定情况相同。例如: ─ Jack likes rice for lunch. —— 杰克午饭喜欢吃米饭。 ─ So do I. —— 我也是。 【 温馨提示 】 “So+ 主语 + 助动词 / 系动词 / 情态动词”表示“确实如此”,表示对上文所述情况的认可和肯定。例如: ─ Jack likes rice for lunch. —— 杰克午饭喜欢吃米饭。 ─ So he does. —— 是啊。(他确实喜欢) 三、 Neither+ 助动词 / 系动词 / 情态动词 + 主语 表示与上文中所述否定情况相同。例如: ─ Peter has never been to Japan. —— 彼得从未去过日本。 ─ Neither have I. —— 我也没有去过。 四、以副词开头的倒装句 以 here, there, out, in, down, away 等表示方位的副词开头的句子中,如果主语是名词,要用倒装句。谓语动词的形式由倒装句句尾的主语决定。例如: There comes the bus . 公交车来了。 Here are the results of the test. 测试结果出来了。 考点五 主谓一致 主谓一致是指谓语动词和主语在人称和数上保持一致,遵循三个原则:①语法一致 ②意义一致 ③就近一致 一、语法一致 是指主语和谓语在语法形式上保持一致,即主语是单数形式,谓语动词用单数形式;主语是复数形式,谓语动词也用复数形式。 1. 主语是以下情况时,谓语动词用单数形式: 不可数名词、可数名词单数、单数代词、不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)、从句等。例如: Coffee is more popular in western countries. 咖啡在西方国家更流行。 Surfing sounds really interesting. 冲浪听起来真的很有趣。 2. 主语是可数名词复数、复数代词,谓语动词用复数形式。例如: Some boys are playing in the park. 一些男孩在公园里玩。 They have been swimming for 2 hours. 他们已经游泳两个小时了。 3. 以 and 和 both. . . and. . . 连接的并列主语是两个或两个以上的人或事物时,谓语动词用复数形式;若并列主语表示同一人或事物( and 后的主语前没有冠词),则谓语动词要用单数形式。例如: Both Linda and her sister are students. 琳达和她妹妹都是学生。 The book and cover is designed by Mike. 书和封面都是迈克设计的。 4. 主语后跟下列词汇时,谓语动词的数和主语保持一致: with, along with, like, except, besides, as well as, together with, including, no less than, rather than, as much as 等。 例如: Jenny with her classmates reads English every morning. 珍妮和同学们每天早上都读英语。 5. a number of + 复数名词作主语时,谓语动词用复数形式; the number of + 复数名词作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式。例如: The number of doctors in the hospital is about 200 and a number of them are women doctors. 这家医院大约有 200 名医生,很多是女医生。 6. “one of + 名词复数 + 单数谓语动词”表示“ …… 之一”。例如: One of my pen pals is from Sydney. 我的笔友中有一位来自悉尼。 7. none of 后面只能跟可数名词的复数形式,谓语动词用单数、复数都可以。例如: None of those books are/is good. 那些书中没有一本是好的。 二、意义一致 是指谓语动词形式要与主语意义上的单复数形式保持一致。例如: 1. 有些集体名词如 family, class, public, group 等作主语时, (1) 若表示一个集体,谓语动词用单数形式; (2) 若表示集体中的成员,谓语动词用复数形式。 例如: ① Our class is on the third floor. 我们班在三楼。 ② Our class are going to visit the museum tomorrow. 明天我们班要去参观博物馆。 2. 有些集体名词如 people, police 等,表示复数意义,谓语动词只用复数形式;有些名词如 news, means, politics 等以 -s 结尾,但表示单数意义,谓语动词用单数形式。例如: The trousers don’t fit me. They are too short. 这条裤子不适合我。它太短了。 3. 复数名词表示时间、长度、重量、价格、距离等意义时,谓语动词用单数形式。例如: Fifty years is a long time in one’s life. 五十年在人的一生中是很长的一段时间。 Three dollars is enough for a pen. 三美元足够买支钢笔了。 4. “the + 形容词”可以表示一类人,作主语时谓语动词用复数形式。例如: The old need more care. 老人更需要关爱。 三、就近一致 是指由部分短语引导主语,谓语动词根据靠近它的主语名词决定单复数形式。 1. There be, Here be 句式的就近原则。例如: There is a book and some pencils on the desk. 桌子上有一本书和几支铅笔。 There are some pencils and a book on the desk. 桌子上有几支铅笔和一本书。 2. Either. . . or. . . , Neither. . . nor. . . , Not only. . . but also. . . 引导主语时的就近原则。例如: Either you or your brother has forgotten to turn off the light before going to bed. 不是你就是你弟弟睡觉前忘了关灯。 Not only Tom but (also) his parents enjoy swimming. 不仅汤姆,而且他的父母也都喜欢游泳。 Ⅰ. 单项选择 1. ( 2012· 铜仁中考) —Is this a Chinese book or an English book? —Oh, _______. A. Yes, it is B. No, it isn’t C. An English book D. A music book 【 解析 】 选 C 。对于选择疑问句的回答,只能选其一,故选 C 。 2. ( 2012· 黔西南州中考) —When I was five, I drew very well. — _______. A. So did I B. So was I C. So I was D. So I did 【 解析 】 选 A 。由上下文主语不一致知用倒装语序,再由上一句的时态为一般过去时,且谓语动词为实义动词 drew, 故倒装语序中用助动词 did 。因此答案为 A 。 3. ( 2012· 自贡中考) —A subway will be built in our hometown before 2015. — _______! Will it pass my house? A. What an excited news B. What exciting news C. How exciting news 【 解析 】 选 B 。 news 是不可数名词,故用 what 引导感叹句。 4. ( 2012· 荆州中考) —How _______ will the boss be back? —In these days. A. far B. soon C. long D. often 【 解析 】 选 B 。由答语是 in 引导的时间状语,可知用 how soon 进行提问。 5. ( 2012· 恩施中考) —It’s sunny today. Let’s go mountain climbing, _______? —Good idea! A. shall we B. will you C. won’t you 【 解析 】 选 A 。 let’s 引导的祈使句其反意疑问句用 shall we 。 6. ( 2012· 黄石中考) They can hardly speak English, _______? A. can’t they B. won’t they C. can they D. will they 【 解析 】 选 C 。 hardly 是否定副词,故用肯定形式进行反意疑问,故选 C 。 7. (2012· 达州中考 )—I have never been to Hawaii. What about Mike? — ________. A. So has he B. So he does C. Neither he has D. Neither has he 【 解析 】 选 D 。由上文“我从没去过夏威夷。”是否定内容可知应该用 neither 引导,再由上下文主语不一致,因此用倒装语序,故选 D 。 8. (2011· 济南中考 )— _______ interesting the storybook is! —Yes. I have read it twice. A. What a B. What C. How a D. How 【 解析 】 选 D 。考查感叹句的用法。根据句意: —— 这本故事书是多么有趣呀! —— 是的。我已经读了两遍了。可以推知符合“ How+ 形容词 + 主语 + 谓语!”的感叹句的结构。故选 D 。 9. ( 2011· 滨州中考) ________ wonderful news report he wrote! All of us were proud of him. A. What a B. What C. How D. How a 【 解析 】 选 A 。考查感叹句。结合感叹句结构故先排除 D ,句中的中心词是可数名词 report , how 后接中心词应该是形容词。故排除 B 和 C 。故选 A 。 10. ( 2011· 阜康中考) — ________ today! —Yes. Shall we have a picnic in the open air? A. What fine weather is B. How fine weather it is C. What a fine weather it is D. How fine the weather is 【 解析 】 选 D 。考查感叹句。感叹句的构成① what+ adj . + 可数名词复数 + (主) + (谓)② what+a/an+ adj . + 可数名词单数 + (主) + (谓)③ How+ adj . / adv . +( 主 )+ (谓),故选 D 。 11. ( 2011· 乐山中考) — _______ is it from Leshan to Chengdu? —I’m not sure, but it takes about two hours to get there by bus. A. How soon B. How far C. How fast 【 解析 】 选 B 。由答语“我不确定,但是乘车去那里大约花费两个小时。”可知对方询问的是从乐山到成都的距离,故用 how far 进行提问。故选 B 。 12. ( 2011· 内江中考) — _______ do you speak English so well? —Because I practice it with my partner every day. A. Why B. When C. Who 【 解析 】 选 A 。由答语是 because 引导的原因状语从句可知上文询问的是“你为什么英语说得这么好?”故选 A 。 13. ( 2011· 广安中考) —How much is the pair of shoes? —Twenty dollars _______ enough. A. is B. are C. am 【 解析 】 选 A 。表示时间、距离、价格、重量、长度等名词或短语作主语时,通常把它作为一个整体概念,谓语动词用单数。故选 A 。 14. ( 2011· 黄石中考) Don’t make so much noise. Lily, _______? A. do you B. don’t you C. will you D. won’t you 【 解析 】 选 C 。考查反意疑问句的用法。否定祈使句的反意疑问句用“ will you” ,故选 C 。 15. ( 2011· 黄冈中考) —Mr. Wang’s never been to Canada, has he? — _______. He went there on business last week. A. No, he hasn’t B. Yes, he has C. No, he has D. Yes, he hasn’t 【 解析 】 选 B 。由答语第二句“上个周他去那里出差了。”可知王先生去过加拿大。故用 Yes, he has. 作答。故选 B 。 16. ( 2011· 铜仁中考) Neither my father nor my mother _______ rock music. They think that it’s too _______. A. like; noise B. likes; noise C. like; noisy D. likes; noisy 【 解析 】 选 D 。 neither. . . nor 连接并列主语时谓语动词和最近的主语保持一致; noise“ 噪音”,是名词,不可被副词 too 修饰; noisy“ 嘈杂的;喧闹的”,是形容词,可以被副词 too 修饰。故选 D 。 17. ( 2011· 福州中考) — Li Mei usually helps others, _______? — Yes, she is kind-hearted. A. does she B. is she C. doesn’t she 【 解析 】 选 C 。反意疑问句的时态和人称主要由陈述部分决定,同时遵守“前肯后否,前否后肯”的原则。故选 C 。 18. ( 2011· 德州中考) —I haven’t seen the film Pirates of the Caribbean: On Stranger Tides . — ________. A. Neither have I B. So have I C. Neither I have D. So I have 【 解析 】 选 A 。由上句是否定情况可排除 B 、 D 两项,用 neither 引导;再由主语不一致可知应该用倒装结构,故选 A 。 19. ( 2011· 贵港中考) —I hope the summer vacation will come soon. — _______. It’s really relaxing. A. So I did B. So I do C. So did I D. So do I 【 解析 】 选 D 。考查 so 引导的倒装句。根据答句中“它真的非常令人放松”可判定答语表示“我也希望”。若表示后者也具有上文提到的情况,用倒装句 so+ 助动词 + 主语,由上句的时态是一般现在时态可知选 D 。 20. ( 2011· 广东中考) —Alice had nothing for breakfast this morning, _______? —No. She got up too late. A. had she B. hadn’t she C. did she D. didn’t she 【 解析 】 选 C 。 nothing 是否定代词,故反问部分用肯定形式,再由谓语动词是实义动词 had ,故用助动词 did 进行反问,故选 C 。 21. ( 2011· 安徽中考) Hey, Nick. _______ comes the last bus! Hurry up, or we’ll have to walk home. A. This B. There C. That D. It 【 解析 】 选 B 。以 here , there 开头的句子,且主语是名词时用倒装语序。故选 B 。 22. ( 2011· 绵阳中考) The number of books in the bookshop is about 10, 000 and a number of them _______ about science. A. is B. was C. are D. were 【 解析 】 选 C 。“ a number of+ 复数名词”意为“许多;大量的”,其修饰的短语作主语时,谓语动词用复数形式,再由时态为一般现在时可知答案为 C 。 Ⅱ. 句型转换 1. ( 2012· 自贡中考) Martin used to give his mother a lot of trouble. ( 改为否定句 ) Martin ______ ______ to give his mother a lot of trouble. 2. ( 2011· 临沂中考) Alice has a tennis racket. ( 改为一般疑问句 ) ______ Alice ______ a tennis racket? 答案: 1. didn’t use/used not 2. Does; have 3. ( 2011· 安顺中考) The students will learn the group dance on the school playground . ( 对画线部分提问 ) ______ ______ the students learn the group dance? 4. ( 2011· 上海中考) The beach is a nice place for tourists. ( 改为感叹句 ) ______ ______ nice place the beach is for tourists! 答案: 3. Where will 4. What a 5. ( 2011· 乌鲁木齐中考) She hardly knew how to solve this math problem. ( 改为反意疑问句 ) She hardly knew how to solve this math problem, ______ ______? 6. ( 2011· 乐山中考) We will turn off the lights for an hour on Earth Day . ( 对画线部分提问 ) ______ ______ we turn off the lights for an hour? 答案: 5. did she 6. When will查看更多