- 2021-05-18 发布 |
- 37.5 KB |
- 14页


申明敬告: 本站不保证该用户上传的文档完整性,不预览、不比对内容而直接下载产生的反悔问题本站不予受理。
文档介绍
2019届一轮复习外研版必修四Module4GreatScientists单元教案设计(14页word版)
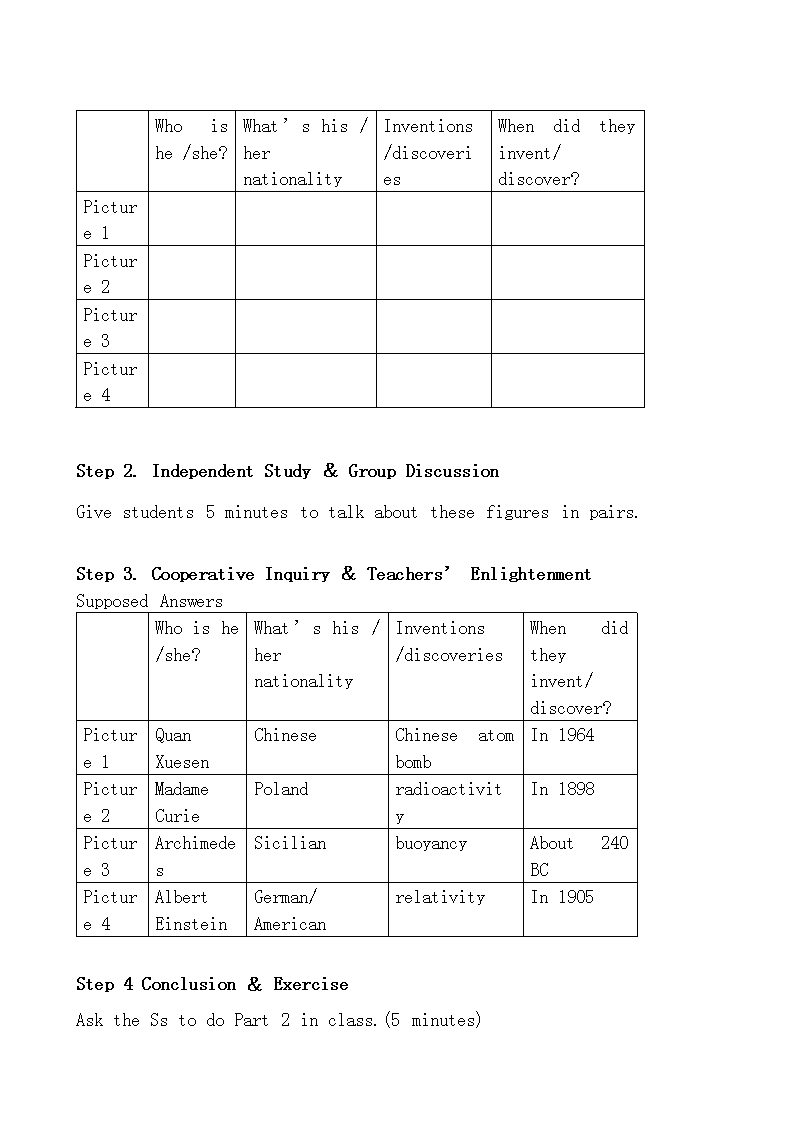
2019届一轮复习外研版必修四Module 4 Great Scientists单元教案设计 Period 1 Introduction I. Teaching Aims Have a good mastery of some words related to science and scientists Talk about great scientists and their achievements II. Teaching Important Points Teach the Ss how to describe a famous scientist. III.Teaching Difficult Points a. Enable the Ss to talk about great Scientists and their achievements: What is his / her name? What did he / she discover or invent? When did he / she discover or invent it? b. Enable the Ss to understand some scientific terms by matching them and their definitions. c. Enable the Ss to write some facts about a famous scientist. IV.Teaching & Learning Methods a. Pairs work and group work; b. Discussion. V.Teaching Procedures Step 1. Lead-in & Question Presentation Use some pictures which can show the rapid developments in our country to raise questions and then introduce our topic, “Great Scientists”. Questions: 1:What do you think made our country develop so fast? 2:Who make science and technology develop? Then turn to Page 31 and look at the pictures in it. Let students talk about them in pairs. Before talking, the teachers show the following table to help them. Who is he /she? What’s his / her nationality Inventions /discoveries When did they invent/ discover? Picture 1 Picture 2 Picture 3 Picture 4 Step 2. Independent Study & Group Discussion Give students 5 minutes to talk about these figures in pairs. Step 3. Cooperative Inquiry & Teachers’ Enlightenment Supposed Answers Who is he /she? What’s his / her nationality Inventions /discoveries When did they invent/ discover? Picture 1 Quan Xuesen Chinese Chinese atom bomb In 1964 Picture 2 Madame Curie Poland radioactivity In 1898 Picture 3 Archimedes Sicilian buoyancy About 240 BC Picture 4 Albert Einstein German/ American relativity In 1905 Step 4 Conclusion & Exercise Ask the Ss to do Part 2 in class.(5 minutes) Homework 1. Preview the Reading in Part 9 in Workbook: finish Parts 10 and 11. 2. Preview the text about Yuan Longping. Teaching Reflection Period 2 Reading I. Teaching Aims Help Ss learn how to talk about Yuan Longping and his achievements. II.Teaching Important Points a. Talk about “the father of hybrid rice—Yuan Longping”: When and where was he born? Why was he famous? What did he discover? How important is the discovery? b. Discuss the question of comprehension: Why is Yuan Longping’s discovery very important? I. Teaching Difficult Points a. Understand the importance of scientists’ achievements. b. Discuss the questions: What would you think of the new hybrid rice if you are a rice farmer? Is the title of the passage suitable? And give the reasons. c. Discuss what the students can learn from Yuan Longping. IV.Teaching & Learning Methods a. Skimming and scanning; b. Asking-and-answering activity in understanding the text; c. Discussion. V.Teaching Procedures Step 1. Lead-in & Question Presentation Questions:1.Do you have a general idea about Yuan Longping? 2.Have you finished reading the text on Page 32? Now you have got a general idea about the great scientist —Yuan Longping. Step 2. Independent Study & Group Discussion Get the Ss to comprehend the passage quickly and accurately and meanwhile help the Ss to form a good habit of reading. Get the general ideas of the passage.(4 minutes) Step 3. Cooperative Inquiry & Teachers’ Enlightenment Read the text again and then work together with their partners to answer some questions. Give them a few minutes to find out the answers and talk about them with their partners.(6 minutes) Questions: 1. What kind of student was Yuan Longping when he was young? 2. Why is he the leading figure in the rice-growing world? 3. What did he discover? 4. How important is the discovery? Step 4. Conclusion & Exercise Who Father of Hybrid Rice—Yuan Longping What His discoveries: hybrid rice of different species How outstanding A leading figure in this field When In 1970 Where In China and other countries Ask the Ss to do Part 2 in class.(5 minutes) Homework Retell the life and achievements of Professor Yuan using about 100 words. Think about: what can you learn from professor Yuan? Possible version: Professor Yuan Longping was “a student who asks questions” and he was interested in plants at the early age. Later he taught and did research in college.In 1970, he discovered a naturally sterile male rice plant. With the support of the government and the help of other researchers, he succeeded in increasing the yield of the rice not only in China but also in other countries. Professor Yuan’s distinguished life’s work has caused many to call him the “Father of Hybrid Rice,” while as a leading figure in this field, his continuing research offers even more promise for world food security and adequate nutrition for the world’s poor. Teaching Reflection Period 3 Language Points I. Teaching Aims Help Ss to have a good mastery of some words related to hybrid rice. Enable the Ss to understand the details about the passage, choosing the correct answer according to the text. II.Teaching Important Points Key words: staple, producer, leading, figure, educate, agriculture, breeding, species, yield, original, publish, sterile, breakthrough, support, production, convert, export, hybrid, agricultural, replace, quality, quantity, bring up, as a result of, cash crop III.Teaching Difficult Points Understand the following sentences: 1. In the rice-growing world, the Chinese scientist, Yuan Longping, is a leading figure. P32 2. He thought there was only one way to do this———by crossing different species of rice plant, and then he could produce a new plant which could give a higher yield than either of the original plants. P32 3. As a result of Yuan Longping’s discoveries Chinese rice production rose by 47.5 percent in the 1990’s. P32 I. Teaching & Learning Methods a. Understand sentences in the whole context; b. Learn these words by explanation and comparison. V.Teaching Procedures Step 1. Lead-in & Question Presentation Turn to Page 32. Let’s look at the sentences: 1. In the rice-growing world, the Chinese scientist, Yuan Longping, is a leading figure. In this sentence, “Yuan Longping” is used as appositive. eg. Shanghai, an international commercial city, lies on the east coast of the Pacific Ocean. 2. He thought there was only one way to do this—by crossing different species of rice plant, and then he could produce a new plant that could give a higher yield than either of the original plants. This sentence is long, so we should learn how to analysis this kind of long, different and complex sentences to comprehend the passage. 3. As a result of Yuan Longping’s discoveries Chinese rice production rose by 47.5 percent in the 1990’s. 1) as a result of = because of = thanks to = owing to = due to 2) rise vi. → rise by =increase by; “by” means “to the extent of”. eg. The bullet missed me by two inches. It needs to be longer by two feet. 3) “In the 1990’s” can also be written as “in the 1990s”. Step 2. Independent Study & Group Discussion Ask the students to read the passage silently by and then to discuss with their partners to make an interview. “Suppose one of you is a sixty-year-old farmer who has been growing rice; One is professor Yuan and the other one is a CCTV reporter. Please talk about the influence of the new hybrid rice.” Step 3. Cooperative Inquiry & Teachers’ Enlightenment Give several minutes for the students to prepare ,then ask three pairs to act it out. Step 4. Conclusion & Exercise Ask the Ss to do Part 4 in class.(5 minutes) Homework Ask the Ss to do Part 3 after class. Teaching Reflection Period 4 Grammar I. Teaching Aims Help Ss learn how to talk about Yuan Longping and his achievements. II.Teaching Important Points a. The usage of passive voice, using “by+ -ing” b. Pay attention to the different tenses of passive voice. III.Teaching Difficult Points a. How to teach the Ss to master the usage of passive voice, using “by+ -ing” b. Change a complex sentence into a simple sentence, using “by+ -ing” IV.Teaching & Learning Methods a. Teach grammar in real situations; b. Learn grammar through practice. V.Teaching Procedures Step 1. Lead-in & Question Presentation Check Ss’ homework. Ask several students to retell the text. Questions: What do you learn from Professor Yuan? Step 2. Independent Study & Group Discussion Review passive voice and learn to use “by+ -ing form”. Turn to Page 33 and read the sentences in the first part and then answer the questions after them. Leave enough time for the Ss to do the exercise, then check the answers all by themselves , talking about the important ones if necessary. Step 3. Cooperative Inquiry & Teachers’ Enlightenment Look at part one on Page 35. Then ask them to do Part 2. Get them to summarize the rues of Direct Speech and Indirect Speech. Guide them to get conclusions from practice. Step 4. Conclusion & Exercise Find out what we have talked about this period, give each an example; Or summarize the rules of them separately. Ask the Ss to write down what they have got and then present it. Homework Translate the following sentences: 1. 英语在全世界被广泛使用。 2. 那家商店昨天被盗了。 3. 在此处将建更多的工厂。 4. 好多良田已经被占用。 5. 只有通过长期的努力,你才会实现自己的目标。 6. 我们可以通过每日的练习来提高口语。 Teaching Reflection Period 5 Cultural Corner I. Teaching Aims a. Enable the Ss to discuss the invention of rocket: When and where were rockets invented? How were rockets invented? How were rockets used in the early stage? b. Enable the Ss to get the general idea of each paragraph. c. Enable the Ss to get to know what we can learn from Stephen Hawking. II.Teaching Important Points Talk about more great scientists and great inventions in history. III. Teaching Difficult Points a. Discuss the answers to the questions. b. Talk about Stephen Hawking’s achievements. IV.Teaching & Learning Methods a. Fast reading; b. Dealing with comprehension questions; c. Discussion; d. Student-centered vocabulary learning. V.Teaching Procedures Step 1. Lead-in & Question Presentation Check the homework. Three minutes for the students to read and find out the main idea of each paragraph. Finish Part 3 on this page. Step 2. Independent Study & Group Discussion Group Discussion: What can we get from the achievement of Stephen Hawking? Come to the other passage--- rockets. Questions about the passage: 1. How were rockets invented? 2. What are they used for today? Step 3. Cooperative Inquiry & Teachers’ Enlightenment The topic sentences of each paragraph. (4 minutes) Step 4. Conclusion & Exercise A supplementary reading material about the passage. The earliest solid rocket fuel was a form of gunpowder, and the earliest recorded mention of gunpowder comes from China late in the third century before Christ. Bamboo tubes filled with saltpeter, sulphur and charcoal were tossed into ceremonial fires during religious festivals in hopes the noise of the explosion would frighten evil spirits. Certainly by the year 1045 AD--21 years before William the Conqueror would land on the shores of England--the use of gunpowder and rockets formed an integral aspect of Chinese military tactics. A point of confusion arises tracing the history of rocketry back before 1045. Chinese documents record the use of “fire arrows,” a term which can mean either rockets or an arrow carrying a flammable substance. The rocket seems to have arrived in Europe around 1241. Homework Collect as much information as possible about rockets or Stephen Hawking. Try to look for some biographies about great scientists to read. Teaching Reflection Period 6 Writing I. Teaching Aims a. Enable Ss to write a biography of Albert Einstein, using the given notes. b. Enable Ss to write a biography of Madame Curie, using the information got from the listening material. II.Teaching Important Points Teach Ss how to write a biography, following the examples. III. Teaching Difficult Points Teach Ss how to write a biography. IV.Teaching & Learning Methods Following the examples; Discussion. V.Teaching Procedures Step 1. Lead-in & Question Presentation Check the homework, asking them to talk about rockets freely. Question: 1. Where did you get the information about Hawking? Step 2. Independent Study & Group Discussion Questions: 1. Do you know how to write a biography of a famous person? 2. How about the structure? Step 3. Cooperative Inquiry & Teachers’ Enlightenment Ask the Ss to write a biography of a famous scientist — Albert Einstein by using the given information. First, let the Ss discuss how to make an outline. Second, teacher shows the instructions on how to write a proposal letter on the screen. Third, ask the Ss to read the notes on Page 37.Ask them to discuss what evaluation should be given. Fourth, give them ten minutes to write a biography. At last, ask some of the Ss to read their biography for the class and the teacher gives some comments. Step 4. Conclusion & Exercise Albert Einstein, born in Ulm, 1879, was probably the most brilliant scientist of the twentieth century. He couldn’t speak until he was three, but he loved mathematics and had the idea of his theory of relativity when he was 16. Albert Einstein studied physics in Zurich, Switzerland. Later he got a job in an office to earn his living. In 1905, he published the special theory of relativity. Four years later, he became an university teacher. By working hard, he published the general theory of relativity in 1915. As a result of his outstanding achievement, he was awarded Nobel Price for physics in 1921. Unfortunately, when Hitler came to power, Albert Einstein was forced to leave his homeland for the U.S. and worked there. Later he took American nationality and died there in 1955. Homework Ask the Ss towrite a biography of Madame Curie, following one of Albert Einstein. Teaching Reflection查看更多