- 2022-02-10 发布 |
- 37.5 KB |
- 8页


申明敬告: 本站不保证该用户上传的文档完整性,不预览、不比对内容而直接下载产生的反悔问题本站不予受理。
文档介绍
小学五年级英语语法知识汇总
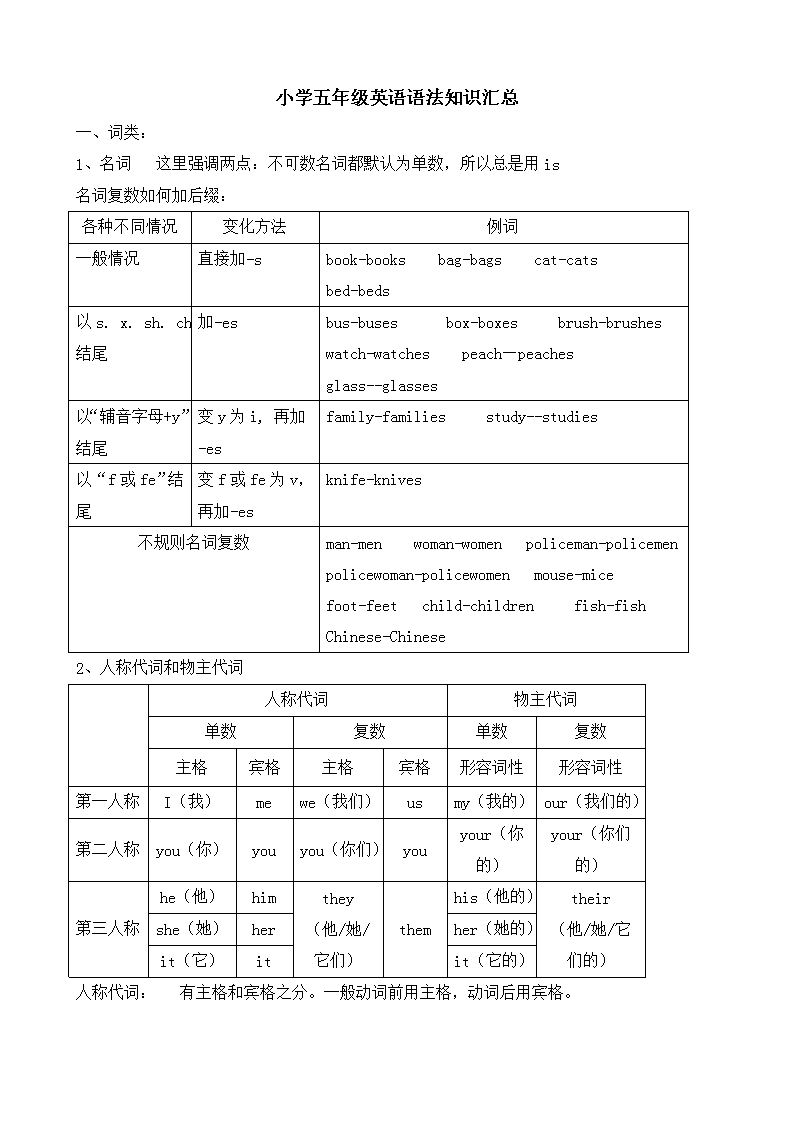
小学五年级英语语法知识汇总 一、词类: 1、名词 这里强调两点:不可数名词都默认为单数,所以总是用is 名词复数如何加后缀: 各种不同情况 变化方法 例词 一般情况 直接加-s book-books bag-bags cat-cats bed-beds 以s. x. sh. ch结尾 加-es bus-buses box-boxes brush-brushes watch-watches peach—peaches glass--glasses 以“辅音字母+y”结尾 变y为i, 再加-es family-families study--studies 以“f或fe”结尾 变f或fe为v,再加-es knife-knives 不规则名词复数 man-men woman-women policeman-policemen policewoman-policewomen mouse-mice foot-feet child-children fish-fish Chinese-Chinese 2、 人称代词和物主代词 人称代词 物主代词 单数 复数 单数 复数 主格 宾格 主格 宾格 形容词性 形容词性 第一人称 I(我) me we(我们) us my(我的) our(我们的) 第二人称 you(你) you you(你们) you your(你的) your(你们的) 第三人称 he(他) him they (他/她/它们) them his(他的) their (他/她/它们的) she(她) her her(她的) it(它) it it(它的) 人称代词: 有主格和宾格之分。一般动词前用主格,动词后用宾格。 3、指示代词 指近处 指远处 单数 this (这个) that (那个) 复数 these(这些) those(那些) 4、冠词 有a、an、the。a和an的区别:an用于元音音素(一般就是元音字母a、e、i、o、u)前,a用于辅音音素前。 二、否定句: be动词(am、is、are)+not、 情态动词can+ not、 助动词(do、does) + not 如何将一个肯定的陈述句改为否定句: 1、看句中有无be动词,如有,直接在be动词后+ not。 2、看句中有无情态动词,如有,直接在情态动词后+ not。 3、如上述二者都没有,就应用助动词+ not。分四个步骤: (1)肯定陈述句中本来是没有助动词的,要加上去,位置在主语(某人或某物)后,动词前。 (2)确定助动词用do、does,根据句中动词,动词是原形的助动词就用do,动词是第三人称单数的助动词就用does, (3)在助动词后加not。 (4)原句中动词假如发生变化就要恢复成原形。 强调一点,有some的要考虑是否要用any。 三、一般疑问句。 如何将一个肯定的陈述句改为一般疑问句: 1、看句中有无be动词,如有,把be动词提到句首即可。 2、看句中有无情态动词,如有,把情态动词提到句首即可。 3、如上述二者都没有,就应把助动提到句首。分四个步骤: (1)肯定陈述句中本来是没有助动词的,要加上去,位置在主语(某人或某物)后,动词前。 (2)确定助动词用do还是does,根据句中动词,动词是原形的助动词就用do,动词是第三人称单数的助动词就用does (3)把助动词后提到句首。 (4)原句中动词假如发生变化就要恢复成原形。 强调一点,有some的要考虑是否要用any。 四、特殊疑问句。表示疑问,有疑问词(在开头),回答有很多种可能。 常用疑问词: 疑问词 意思 用法 What time 什么时间 问具体时间,如几点钟 Who 谁 问人 Whose 谁的 问主人 Where 在哪里 问地点 What 什么 问东西、事物 What colour 什么颜色 问颜色 How old 多大年纪 问年纪 How many 多少数量(可数名词) 问数量 How much 多少钱;多少数量(不可数名词) 问多少钱或数量(不可数) 五、时态 1、一般现在时 (1)一般现在时中的be动词: 一般用原形:am is are am用于第一人称单数(I);is用于第三人称单数(he she it和其他人名或称谓,如:Ben his sister等);are用于第二人称单数(you)和所有复数(包括第一人称复数we、第二人称复数you;第三人称复数they和其他复数,如the children 、 his parents等)。 (2)一般现在时中的动词: 第一种情况:主语是第三人称单数(he she it 和其他,如Helen 、her cousin 等),动词后一般加s或es。 第二种情况:主语不是第三人称单数,动词都用原形。 (4)一般现在时判断依据(如何判断一个句子是一般现在时): △be动词是am、is、are △动词用原形或加s、es △没有时间状语或有usually、often、everyday、sometimes等不是具体的时间 2、现在进行时 (1)构成形式:Be动词+动词的ing形式 这里强调一点,两者缺少其中任何一种都不可以构成现在进行时。 (2)现在进行时表示动作正在进行或事情正在发生。 (3)有用的依据:一个句子中既有be动词,又有动词,且动词加了ing ←→ 该句是现在进行时 (4)句中往往有now、look、listen等词。 动词现在分词的变化见下表: 词尾情况 变化方式 例词 一般情况 加—ing play玩—playing do做—doing go去—going jump跳—jumping sing唱—singing ski滑雪—skiing see看见--seeing 以不发音的e结尾 去e加—ing make做—making take拿到—taking like喜欢—liking come来—coming write写—writing dance跳舞—dancing have有—having close关—closing 以重读闭音节结尾的动词,中间只有一个元音字母,词尾只有一个辅音字母 双写最后一个辅音字母再加—ing swim游泳—swimming sit坐—sitting run跑—running get得到—getting put放—putting begin开始—beginning jog慢跑—jogging 同音词:too---two----to buy---by I---eye four----for龄 there----their right----write sun----son no----know here---hear who’s----whose 近义词: many----a lot of / lots of large----big desk----table photo----picture lamp----light like----love 反义词或对应词:old----new go----come big----small open----close black----white here----there 完整形式:let’s=let us(让我们) I’d=I would can’t=can not I’m=I am 词性变换:one(序数词) first monkey(复数)monkeys skiing(原形)ski is(复数)are families(单数)family make(现在分词)making we are(缩略形式)we’re do(第三人称单数)does have(第三人称单数)has photo(复数)photos fat(反义词)thin 做题目时一定要记住: 1. can+动词原形 2. like+动词ing 3. like+名词复数 4. play+足球类 play the +乐器类 5. how many +名词复数 6. would like +to+动词原形 7. let’s+动词原形 8. 现在进行时:be(am,is,are)+动词ing 9. 动词第三人称单数形式 3、 一般过去时 定义:表示过去发生的行为或状态,这种时态往往都有一个明确的过去时间状语,如:yesterday,last week(month,year)等,或联系上下文能确切知道行为发生在过去,其谓语用过去式。 (1)一般过去时中的be动词:was were was用于第一人称(I)和第三人称单数(he she it和其他人名或称谓),were用于第二人称单数(you)和所有复数(包括第一人称复数we、第二人称复数you;第三人称复数they和其他复数,如the children 、 his parents等)。 (2)在动词1、基本形式:am、are、is (1) am 第一人称I+am (注意:“I”无论何时都要大写,不管位于句首还是句中) 例:I am a beautiful girl. I am twenty. (2) are 第二人称you+are; 一人称复数we+are; 三人称复数they+are 其他复数名词+are (注意:第二人称单复数同形,都为you) 例:You are my good friend. We are in the same class. They are on the road. The books are on the desk. (3) is 第三人称he(男) +is ; she(女)+is; it(不是人)+is;其他单数名词+is 例:HeShe is a good student. It is a white cat. A dog is on that street. 后面加ed。 动词过去式的构成规则: 一般情况,直接加ed,clean—cleaned,finish—finished,want—wanted,watch—watched。 以不发音字母“e”结尾的加d,move—moved,live—lived,arrive—arrived。 以“辅音字母+y”结尾的,变y为i,再加ed,study—studied,cry—cried,try—tried。注意,“以元音字母+y”结尾的,直接加ed,play—played。 以重读闭音节结尾,结尾只有一个元音字母加一个辅音字母的,双写最后一个辅音字母再加ed。是stop—stopped,drop—dropped。 (3)一般过去时的句型: 否定句:be动词(was were)+not、 助动词(did) + not+动原 疑问句:was/were +主+其他? Did +主+动原+其他? 特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句? 一课时:be 动词 主讲与人称代词的搭配 1、基本形式:am、are、is (1) am 第一人称I+am (注意:“I”无论何时都要大写,不管位于句首还是句中) 例:I am a beautiful girl. I am twenty. (2) are 第二人称you+are; 一人称复数we+are; 三人称复数they+are 其他复数名词+are (注意:第二人称单复数同形,都为you) 例:You are my good friend. We are in the same class. They are on the road. The books are on the desk. (3) is 第三人称he(男) +is ; she(女)+is; it(不是人)+is;其他单数名词+is 例:HeShe is a good student. It is a white cat. A dog is on that street. 2、肯定、否定、疑问(等于号后是简写) 肯定 否定——be动词后加not 一般疑问——be动词移到主语前 一般疑问否定 一般疑问回答 肯定和否定 I am… =I’m …. I am not… =I’m not ... Am I…? Am not I…? Yes,I’m. No,I’m not. You are… = you’re… You are not… =You aren’t… Are you…? Are not you...? =Aren’t you…? Yes,you are. No,you are not. SheHeIt is…= SheHeIt’s SheHeIt is not… =SheHeIt isn’t… Is sheheit…? Is not sheheit…? =Isn’t sheheit…? Yes,sheheIt is. No,sheheIt is not. We are =We’re We are not… =We aren’t… Are we…? Are not we…? =Aren’t we…? Yes,we are. No,we are not. They are =They’re They are not… =They aren’t Are they…? Are not they…? =Aren’t they…? Yes,they are. No,they are not. 例:I am(not) from London. My eyes are(not) small. My hair is(not) long. Am I a Chniese? 回答: 肯定:Yes, you are. 否定: No, you aren’t. Is the cat fat? 回答:肯定:Yes, it is. 否定: No, it isn’t. 注意:在一般疑问回答中,肯定回答除I’m不可简写,否定回答均可简写。 另:特殊疑问句中:wherehowwhowhatwhy+be动词+人称代词或名词? 例:What is your name? My name is GaoBuHan. Where are you? I’m in the classroom. 3. 总结:Be的用法口诀 I用am;you、we、they 都 用are;is连着he,she,it; 单数名词用is,复数名词全用are。 变疑问,往前提,句末问号莫丢弃。 变否定,更容易,be后not莫忘记。 疑问否定任你变,句首大写莫迟疑。查看更多