- 2022-08-23 发布 |
- 37.5 KB |
- 23页

申明敬告: 本站不保证该用户上传的文档完整性,不预览、不比对内容而直接下载产生的反悔问题本站不予受理。
文档介绍
语言学522-524
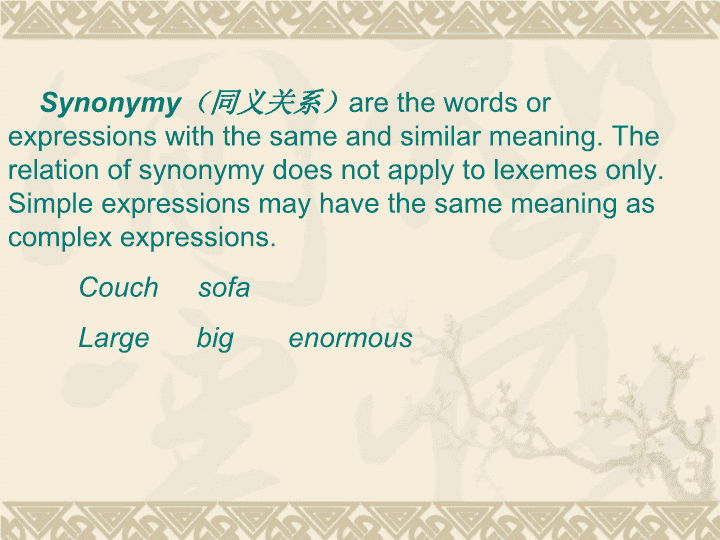
Semanticrelations5.2.2—5.2.4\nContents:1.SynonymyandAntonymy2.MeronymyandHyponymy3.PolysemyandHomonymy\nSynonymy(同义关系)arethewordsorexpressionswiththesameandsimilarmeaning.Therelationofsynonymydoesnotapplytolexemesonly.Simpleexpressionsmayhavethesamemeaningascomplexexpressions.CouchsofaLargebigenormous\nHowever,truesynonymsarerare.Inmostcases,synonymsmaydifferinoneormoreofthefollowingaspects:DifferenceinoriginInEnglish,therearesomepairsofsynonymsoneofwhichisdevelopedfromthenativewordwhiletheotherisborrowedfromanotherlanguage:nativewordsborrowedwordsanswerreplybodilycorporalSomeEnglishsynonymsmaybelongtowordsofdifferentlinguisticorigin:Anglo-SaxonFrenchLatinAskquestioninterrogate\nSomesynonymsbelongtodifferentgeographicvarieties:BritishEnglishAmericanEnglishTubesubwayB.DifferenceinshadesofmeaningSomesynonymsdifferintheshadesofmeaning.e.g.amazeandastoundSamedenotation:tofillwithgreatsurpriseDifferinthedegreeofincredibility.Accordingtothedifferencesinemotionalflavor,synonymscanbedividedintothreecategories:elevated,neutralandvulgar.\nC.Differenceinsocio-expressivemeaningAccordingtothedifferencesinemotionalflavor,synonymsmayimplyapproval,disapprovalorneutralattitudeofthespeaker.HorseneutralSteedandchargerapprovalNagandplugdisapproval\nD.Differenceinstylisticmeaninge.g.die,perish,decease,expire,begoneandpassawayDieisusedincolloquial,perishisusuallyusedinnews,deceaseisusedwhenconcerningtolawissues,expireisaliteraryEnglishword,andbegoneandpassawayareusedinoralEnglish.\nE.Differenceincollocationanddistributione.g.accuse,charge,rebuke,andreproachCommondenotativemeaning:toblameTheprepositionsco-occurwiththemvarylikethis:accuse…of,charge…with,rebuke…for,reproach…with/for.Othersynonymshavedifferentdistributions\nAntonymy(反义关系)istherelationshipoftheoppositenessofmeaning.Accordingtothesemanticrelationship,antonymscanbelooselydividedintothreecategories:A.ComplementaryantonymsB.GradableantonymsC.Relationalopposites\nComplementaryantonymsQualitativeadj.:dead/aliveNounsdenotingquality,state,orrelationship:wisdom/foolishnessVerbsdenoting“feelings”,emotions,oraction:support/opposeAdverbsdenoting“time”,“positionanddirection”,or“state”:early/late\nGradableantonymsPairsofwordswhose“crucial”semanticfeaturesarelocatedatthedifferentendsofonecontinuum.E.g.big-small.RelationaloppositesPairsoflexemesofexpressionswhosecrucialsemanticsfeaturesdisplayareciprocalrelationship.Onememberofthepairpresupposetheother.Nouns:wife/husbandVerbs:buy/sellPropositions:above/below\nAntonymymayvaryinaccordancewithcollocation.Freshbread/stalebreadFreshair/stuffyairFreshflower/fadedflower\nMeronymy&HyponymyMeronymy(部分-整体关系)isatermusedtodescribeapart-wholerelationshipbetweenlexicalitems.e.g.root,trunk,branch,andleafaremeronymsofatreebecausetheyareintherelationshipofXispartofY.\nHyponymy(上下义关系)isusedtorefertoaspecific-generalsemanticrelationshipbetweenlexicalitems.\nMeronymy&HyponymyThereisnoclearlinebetweenMeronymyandHyponymy.Hyponymydiffersfrommeronymyintransitivity.Hyponymyisalwaystransitiveinthesensethatthereisahierarchicalrelationbetweendifferentterms.Butmeronymymayormaynotbehierarchical.\nPolysemy&HomonymyPolysemy(一词多义):asinglelexemehasseveralmeanings.e.g.chiphasseveralmeanings:“electroniccircuit”(电子芯片),“akindoffood”or“apieceofwood”Polysemycanbesaidtobetheresultfromthechangeofmeaning.\nHomonymy(同音异义词)referstocaseswherelexemeswiththesamephonologicalofmorphologicalshapehavedifferentmeanings.Itmayhaveidenticalpronunciationbutdonotsharecommonsemanticfeatures.e.g.race(contestofspeed)–race(ethnicgroup).\nHomonymycanusuallybeseeninthefollowingtwocases:Homographs(同形异义词):writteninthesamewaybutdifferinmeaningandsometimesinpronunciationorderivation,e.g.Homophones(同音异形异义词)arewordswithidenticalpronunciationbutwithdifferentspellingandmeanings.\nThreereasonsmayaccountfortheappearanceofhomonyms.A.DivergingmeaningdevelopmentSomehomonymsresultfromthesplittingofthedifferentmeaningsofasingleearlierword.\nB.ConvergingsounddevelopmentSomehomonymsresultfromaccidentalconvergingofthesounddevelopmentoftwoofmorewordsofdifferentetymologicalsources.C.ShorteningofthewordsSomehomonymsresultfromthecoincidenceofpronunciationandspellingofpairsofwords,oneofwhichistheshorteningofanotherwordofexpression.\nLyons’twocriteriaA.Theetymologicalcriterion.Itcanjustifythenativespeaker’sintuitivedistinctionoflexemes.B.Therelatednessofmeaning.Themeaningofapolysemhaveoneormoreofthefollowinglogicalrelationsbetweenthem:\nGeneralization:extendedfromspecifictogeneral.Specification:narroweddownfromgeneraltothespecific.Substantiation:fromabstracttosubstantive.Abstraction:fromsubstantivetoabstract.Metaphor:derivenewmeaningwhichhavecertainsimilaritieswiththeoriginalones.Incontrast,themeaningofhomonymsaredistinctlyunrelated.Itismatterofdegree.\nTHANKYOU!查看更多