- 2022-08-11 发布 |
- 37.5 KB |
- 7页


申明敬告: 本站不保证该用户上传的文档完整性,不预览、不比对内容而直接下载产生的反悔问题本站不予受理。
文档介绍
考试大纲(语言学)
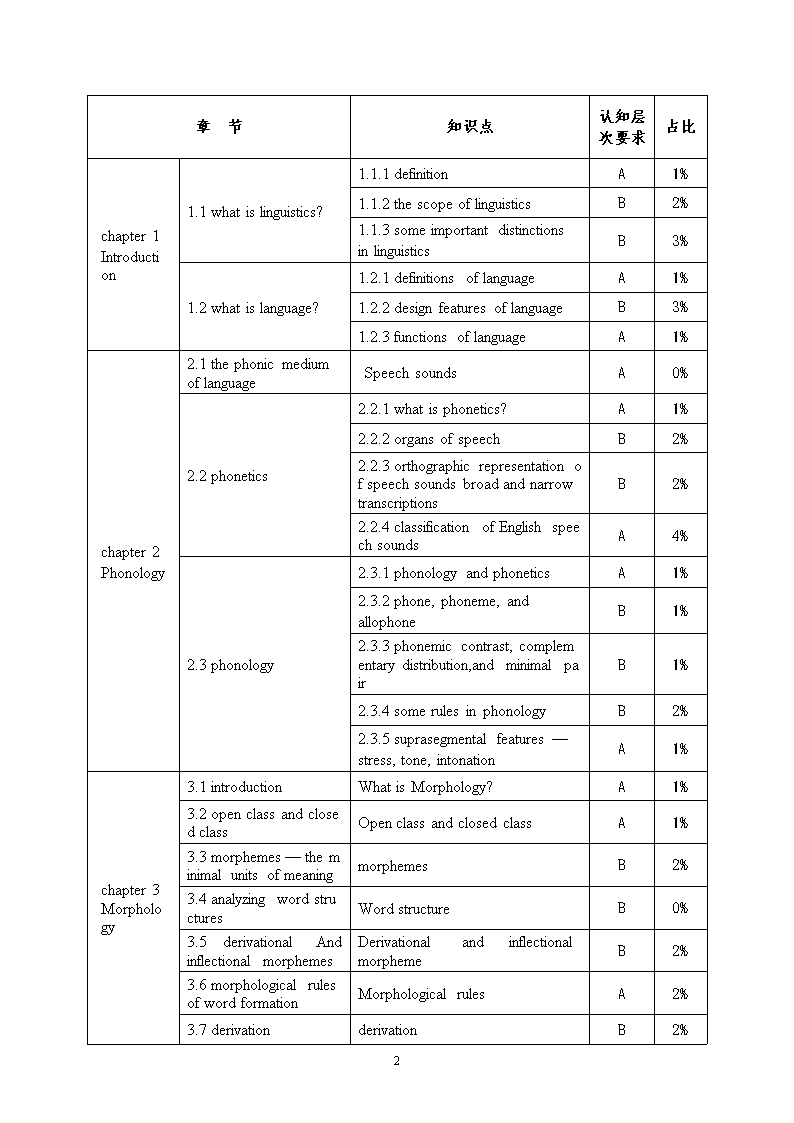
XXXXX学院外国语学院语言学概论考试大纲一、考试基本要求《英语语言学概论》是英语教育专业的一门基础理论课。语言学是主要研究语言的性质、语言的功能、语言的产生和发展、语言的习得以及语言和人类其它活动关系的学科。随着对语言研究的不断深入,人们更多地把注意力集中在语言学研究和语言教学研究的关系上。本课程开设的目的在于促进学生了解英语语言的性质、结构、特征和功能,以及它们与外语教学的关系,从而加强英语语言的学习和英语教学法的研究,提高英语语言水平和英语语言教学能力。二、考试形式考查和考试相结合,语言学概论考试采用闭卷笔试形式,试卷满分为100分,考试时间为120分钟。三、适用专业英语本科专业。四、考试内容和考试要求(按章或按模块分别叙述)考试大纲以教学大纲的要求为依据,对教材及大纲中各部分内容、知识点提出不同层次的要求,具体要求可分为两个层次,分别用A、B表示,其含义如下表:符号层次含义A识汇理解正确记忆并理解所学知识及所学知识的基本特征。B牢固掌握熟练应用能将所学知识在理解基础上,熟练应用,解决一些新的、有一定难度的问题。7\n章节知识点认知层次要求占比chapter 1Introduction1.1 what is linguistics?1.1.1 definitionA1%1.1.2 the scope of linguisticsB2%1.1.3 some important distinctions in linguisticsB3%1.2 what is language?1.2.1 definitions of languageA1%1.2.2 design features of languageB3%1.2.3 functions of languageA1%chapter 2Phonology2.1 the phonic medium of languageSpeechsoundsA0%2.2 phonetics2.2.1 what is phonetics?A1%2.2.2 organs of speechB2%2.2.3 orthographic representation of speech sounds broad and narrow transcriptionsB2%2.2.4 classification of English speech soundsA4%2.3 phonology2.3.1 phonology and phoneticsA1%2.3.2 phone, phoneme, and allophoneB1%2.3.3 phonemic contrast, complementary distribution,and minimal pairB1%2.3.4 some rules in phonologyB2%2.3.5 suprasegmental features —stress, tone, intonationA1%chapter 3Morphology3.1 introductionWhatisMorphology?A1%3.2 open class and closed classOpenclassandclosedclassA1%3.3 morphemes— the minimal units of meaningmorphemesB2%3.4 analyzing word structuresWordstructureB0%3.5derivationalAndinflectional morphemesDerivationalandinflectionalmorphemeB2%3.6 morphological rules of word formationMorphologicalrulesA2%3.7 derivationderivationB2%7\n3.8 compoundscompoundingB2%chapter 4 Syntax4.1 what is syntax?definitionA1%4.2 categories4.2.1 word-level categoriesA1%4.2.2 phrase categories and their structuresB1%4.3 phrase structure rule4.3.1 xpruleB1%4.3.2 coordination ruleB0%4.4 phrase elements4.4.1 specifiersA1%4.4.2 complementsA1%4.4.3 modifiersA0%4.5 sentences (the s rule)SentencestructureB0%4.6 transformations4.6.1 auxiliary movementB1%4.6.2 do insertionB1%4.6.3 deep structure and surface structureB3%4.6.4 wh movementB1%4.6.5 move a and constraints on transformationsA0%chapter 5Semantics5.1 what is semantics?definitionA1%5.2 some views concerning the study of meaning5.2.1 the naming theoryA0%5.2.2 the conceptualist viewA1%5.2.3 contextualismA1%5.2.4 behaviorismA1%5.3 lexical meaning5.3.1 senseand referenceA1%5.3.2 major sense relationsB3%5.4 sense relations between sentencesSentencerelationB1%5.5 analysis of meaning5.5.1 componential analysis — a way to analyze lexical meaningB2%5.5.2 predication analysis-a way to analyze sentence meaningB2%7\nchapter 6Pragmatics6.1 some basic notions6.1.1 definitionA1%6.1.2 pragmatics vs.semanticsA1%6.1.3 contextA1%6.1.4 sentence meaning vs.utterance meaningB2%6.2 speech act theory6.2.1 austin's model of speech actsB1%6.2.2 searle's classification of speech actsB1%6.2.3 indirect speech actsB2%6.3 principle of conversationprinciple of conversationA1%6.4 cross-cultural pragmatic failurecross-cultural pragmatic failureB1%chapter 7Language change7.1 introductionBriefintroductionA0%7.2 phonological changesphonological changesA1%7.3 morphological and syntactic change7.3.1 addition of affixesB0%7.3.2 loss of affixesB0%7.3.3 change of word orderB1%7.3.4 change in negation ruleB0%7.4lexicalandsemanticchange7.4.1 addition of new wordsB0%7.4.2 loss of wordsB0%7.4.3 semantic changesB1%7.5 some recent trends7.5.1 moving towards greater informalityB1%7.5.2 the influence of American EnglishB0%7.5.3 the influence of science and technologyB1%7.6 the causes of language change the causes of language changeA1%7\nchapter 8Language and society8.1 the scope of sociolinguistics8.1.1 the relatedness between language and societyA1%8.1.2 speech community and speech varietyB1%8.1.3 two approaches to sociolinguistic studiesA1%8.2 varieties of language8.2.1 dialectal varietiesA1%8.2.2 registerA1%8.2.3 degree of formalityA0%8.3 standard dialectstandard dialectB1%8.4 pidgin and creolepidgin and creoleA0%8.5 bilingualism and diglosiabilingualism and diglosiaA0%chapter 9Language and culture9.1 introductionBriefintroductionA0%9.2 what is culture?what is culture?A1%9.3 the relationship between language and culturethe relationship between language and cultureB1%9.4 Sapir-whorf hypothesisSsapir-whorf hypothesisA0%9.5 linguistic evidence of cultural differences9.5.1 greetings and terms of addressB0%9.5.2 gratitude and complimentsB0%9.5.3 colour wordsB0%9.5.4 privacy and taboosB0%9.5.5 rounding off numbersB0%9.5.6 words and cultural-specific connotationsB0%9.5.7 cultural-related idioms, proverbs and metaphorsB1%9.6 culture contact, cultural overlap and diffusionculture contact, cultural overlap and diffusionA1%9.7 the significance of cultural teaching and learningthe significance of cultural teaching and learningA1%7\n9.8 intercultural communicationintercultural communicationA1%chapter 10LanguageAcquisition10.1 introductionBriefintroductionA0%10.2 theories of child language acquisition10.2.1 a behaviourist view of language acquisitionB1%10.2.2 an innatist view of language acquisitionB0%10.2.3 an interactionist view of language acquisitionB1%10.3 cognitive development in child language developmentcognitive development in child language developmentA1%10.4 language environment and the critical period hypo-thesislanguage environment and the critical period hypo-thesisA0%10.5 stages in child language development10.5.1 phonological developmentA1%10.5.2 vocabulary developmentA0%10.5.3 grammatical developmentA0%10.5.4 pragmatic developmentA0%10.6 atypical developmentatypical developmentA0%chapter 11 Second Language Acquisition11.1 introductionBriefintroductionA0%11.2 connections between first language acquisition and second language acquisitionconnections between first language acquisition and second language acquisitionA1%11.3 contrastive analysiscontrastive analysisB1%11.4 error analysiserror analysisB1%11.5 interlanguage interlanguageB0%11.6 the role of the native language in second language learningthe role of the native language in second language learningB0%11.7 second language learning models and input hypothesissecond language learning models and input hypothesisA1%11.8 individual differences individual differencesA0%7\n11.9 second language acquisition and its pedagogical implicationssecond language acquisition and its pedagogical implicationsB0%五、主要参考书目教材:《新编简明语言学教程》(第二版),戴伟栋,何兆雄编,上海外语教育出版社,2013年。参考资料:1.《语言学概论》(第一版),杨信彰编,高等教育出版社,2005年;2.《语言学教程》(第四版),胡壮麟编,北京大学出版社,2011年;3.《新编语言学教程》(第一版),刘润清,文旭编,外语教学与研究出版社,2006年;4.《语言学概论》(第一版),蓝纯编,外语教学与研究出版社,2009年;5.《语言学高级教程》(第一版),胡壮麟,姜望琪编,北京大学出版社,2002年;6.J.L.Austin.HowtoDoThingswithWords(第一版).外语教学与研究出版社,2002年;7.JohnR.Searle.ExpressionandMeaning:StudiesintheTheoryofSpeechActs(第一版).外语教学与研究出版社,2001年;8.RonaldWardhaugh.AnIntroductiontoSociolinguistics(第一版).外语教学与研究出版社,2000年。7查看更多