- 2021-05-20 发布 |
- 37.5 KB |
- 81页


申明敬告: 本站不保证该用户上传的文档完整性,不预览、不比对内容而直接下载产生的反悔问题本站不予受理。
文档介绍
2018届二轮复习非谓语动词考点全面解读(共81张PPT)
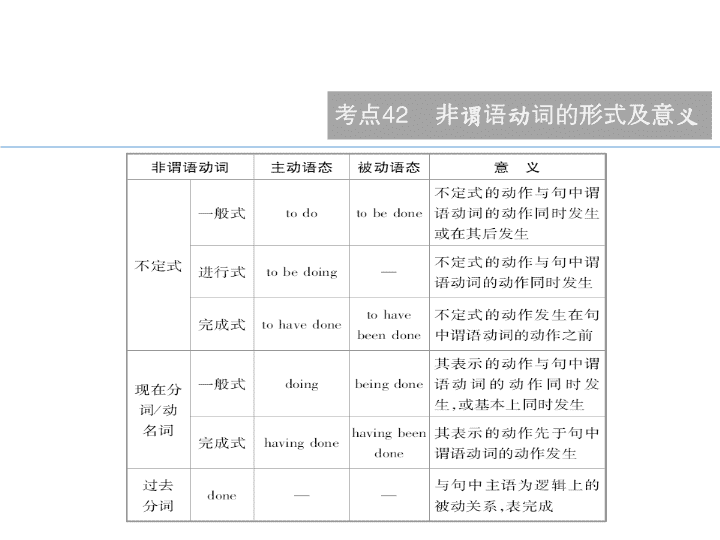
2018 届二轮复习语法专题 非谓语动词考点全面解读 完全掌握 非谓语动词的形式及意义 考点 42 非谓语动词的形式及意义 ·I have a lot of reading to complete before the end of this term. 本学期结束前,我有大量的阅读任务要完成 。 ·It is of help to be doing some exercise out of doors in the morning. 早晨做些户外活动是有益处的。 ·Charles Babbage is generally considered to have invented the first computer. 人们一致认为查尔斯 · 巴比奇发明了第一台计算机。 考点 42 非谓语动词的形式及意义 ·No harm seems to have been done . 似乎并没有造成伤害。 ·Do you mind being interrupted while studying? 你介意学习时被打扰吗? · Not having seen her for a long time, I missed her very much. 很长时间未见到她,我很想念她。 · Given enough time, we are sure to do it well. 如果给予我们足够的时间,我们一定能做好。 考点 42 非谓语动词的形式及意义 考点 43 非谓语动词作状语的用法 分考点 1 不定式作状语 分考点 2 分词作状语 分考点 3 独立成分作状语 分考点 4 独立主格结构作状语 Point 1 分考点 1 不定式作状语 作目的状语,意为“为了”,可以单独放在句首、句中或句末。如果强调目的性,不定式前也可加 in order 或 so as ,但 so as to 不能置于句首。 · To increase levels of community service, some schools have launched compulsory volunteer programs. 为了提高社区服务水平,一些学校 已经发起了义务志愿者服务计划。 [江苏 2015 ] 分考点 1 不定式作状语 · More TV programs, according to government officials, will be produced to raise people’s concern over food safety. 据政府官方表示,为了提高人们对食品安全的关注,将会制作更多的电视节目。 [ 重庆 ] · In order to support his family, Mr. Johnson began to plant herbs and vegetables. 为了养家,约翰逊先生开始种植香草和蔬菜。 [广东 2015 ] · The bus stopped so as to pick up passengers. 公共汽车停下来以便搭载乘客。 Point 2 分考点 1 不定式作状语 作结果状语。不定式作结果状语常表示令人意外的结果 , 常用于下列结构中: 1. only to do 2. enough to do 3. too… to do 4. so/such… as to… 1. 表示意想不到的结果 2. 足够做 …… 3. 太 …… 而不能 …… 4. 如此 …… 以至于 …… 分考点 1 不定式作状语 ·Tom took a taxi to the airport, only to find his plane high up in the sky. 汤姆乘出租车去了机场,结果发现他要乘坐的飞机已飞入高空。 [ 四川 ] ·He is old enough to go to school. 他到上学的年龄了。 ·Mary is too tired to do the job. 玛丽太累了,做不了这项工作了。 Point 3 分考点 1 不定式作状语 作原因状语。形容词作表语时,后可接不定式作原因状语,用以说明产生这种情绪的原因,常用于这类结构的形容词有 sorry, surprised, disappointed, excited, glad, happy, anxious, delighted, pleased, foolish 等。 ·Maggie was glad to be home in her own bed. 马吉回到家躺在自己的床上,觉得非常高兴。 · We were astonished to find the temple still in its original condition. 令我们吃惊的是,这座寺庙仍保持着它最初的样子。 [ 辽宁 ] Point 4 分考点 1 不定式作状语 动词不定式也可以跟在一些作表语的形容词后,构成“主语 + 系动词 + 形容词 +to do” 结构。这类形容词如: easy, difficult, hard, cheap, expensive, fit, comfortable, heavy, good, important, impossible, dangerous 等,表示主语的特征或性质,不定式和句子主语构成逻辑上的动宾关系,不定式常用主动形式表示被动意义。 ·This machine is very easy to operate . Anybody can learn to use it in a few minutes. 这台机器很容易操作。只需几分钟,任何人都能学会使 用。 [辽宁] ·The book is very hard to understand . 这本书很难理解。 分考点 2 分词 作状语 分词包括现在分词和过去分词,现在分词表示的动作与句子主语是逻辑上的主动关系,且含有进行的意义;过去分词表示的动作与句子主语为逻辑上的动宾关系,且含有完成的意义。 分考点 2 分词 作状语 分考点 2 分词 作状语 分考点 2 分词 作状语 分考点 3 独立成分作状语 有些分词或不定式短语作状语,其形式的选择不受上下文的影响,称作独立成分。常见的有: 分考点 3 独立成分作状语 · Judging from her outward appearance, she is very kind. 从她表面上看,她很友好。 · Considering the high quality, our price is very reasonable. 鉴于产品的高质量,我们的价格非常合理。 · To tell the truth , I was frightened to death. 老实说,我怕得要死。 [《 朗文当代 》] 分考点 4 独立主格结构作状语 独立主格结构是由名词或代词加上名词、形容词、副词、介词短语或非谓语动词等构成的一种独立结构,用于修饰整个句子。独立主格结构中的名词或代词与其后的成分构成逻辑上的主谓或动宾关系。独立主格结构可置于句子前、句子末或句子中,常由逗号将其与句子分开,在句中作状语,相当于一个状语从句。 Point 1 名词 / 代词 + 现在分词 / 过去分词 / 不定式 / 名词 / 形容词 / 副词 / 介词短语 · The situation getting worse , they had to ask for help. 事态越来越糟糕,他们只好向他人求救。(表原因) ·He was listening attentively in class, his eyes fixed on the blackboard. 他上课专心听讲,眼睛紧盯着黑板。(表伴随) · No one to wake me up , I might be late for the first class. 如果没人叫醒我,我可能会错过第一节课。(表条件) 分考点 4 独立主格结构作状语 Point 2 with/without+ 复合宾语 “ with/without+ 宾语 + 宾语补足语”结构可以构成独立主格结构,在句中常作伴随状语和原因状语。 (1)“with+ 名词 / 代词 + 现在分词”表主动且进行,或表特征。 ·I couldn’t do my homework with all that noise going on . 由于噪音不断,我做不了作业。 [ 北京 ] 分考点 4 独立主格结构作状语 (2)“with+ 名词 / 代词 + 过去分词”表被动且完成,或表状态。 ·It was a pity that the great writer died with his works unfinished . 真可 惜,这位伟大的作家去世时,他的作品尚未完成。 [ 福建 ] 分考点 4 独立主格结构作状语 (3)“with+ 名词 / 代词 + 动词不定式”表将来。 · With the exception of using a small microwave oven to heat food , students are not permitted to cook in their rooms. 除了允许使用小型 微波炉加热食物之外,禁止学生在他们的房间里做饭。 [天津 2015 ] 分考点 4 独立主格结构作状语 (4)“with+ 名词 / 代词 + 形容词 / 副词 / 名词 / 介词短语”表宾语的性质或状 态。 · With production up by 60%, the company has had another excellent year. 产量上升了 60 %,公司又度过了辉煌的一年。 分考点 4 独立主格结构作状语 考点 44 非谓语动词作定语的用法 分考点 1 不定式作定语 分考点 2 分词作定语 分考点 3 动名词作定语 Point 1 不定式作定语表示将来的动作。 ·I have a lot of things to do . 我有许多事要做。 ·The question to be discussed at the meeting is very important. 将在会议上讨论的那个问题非常重要。 分考点 1 不定式作定语 Point 2 不定式常放在某些名词或代词后作定语。如果作定语的不定式是不及物动词,或者不定式所修饰的名词或代词是不定式动作的地点、工具等,不定式后需要加相应的介词。 ·I’m not sure which restaurant to eat at . 我不确定要在哪家餐馆吃饭。 分考点 1 不定式作定语 【 特别注意 】 如果被不定式修饰的名词为 place, time, way 等,不定式后的介词习惯上可以省去。 ·It took us ages to find a place to live (in) . 我们花了好长时间才找到一个住处。 Point 3 不定式用来修饰被序数词、最高级或 no, all, any 等限定的中心词,且与中心词为逻辑上的主动关系。 ·Jack was the best man to do the job. 杰克是做这项工作的最佳人选。 ·He is always the first to arrive at the school and the last to leave the school. 他总是第一个到校,最后一个离校。 分考点 1 不定式作定语 Point 4 被修饰词是抽象名词时,常用不定式作定语。 常见的该类名词有: ability, chance, idea, hope, wish, fact, excuse, promise, attempt, way 等。 ·The ability to express an idea is as important as the idea itself. 表达观点的能力与观点本身同等重要。 [ 湖南 ] 分考点 1 不定式作定语 【 特别注意 】 不定式作定语时,若句子主语是不定式动作的执行者,则用主动形式表被动含义;若句子主语不是不定式动作的执行者,则用被动形式表被动含义。 ·She has a sister to look after . 她有一个妹妹需要照顾。 (she 是 look after 的执行者 ) ·I want to go to Beijing. Do you have anything to be bought ? 我要去北京。你有什么东西需要买吗? (you 不是 buy 的执行者 ) 分考点 1 不定式作定语 Point 1 分考点 2 分词作定语 作定语的及物动词的分词形式有:现在分词、“ being + 过去分词”、过去分词。当被修饰的名词与分词之间为主动关系时,用现在分词;当被修饰的名词与分词之间为被动关系且表正在进行时,用“ being + 过去分词”;当被修饰的名词与分词之间为被动关系且表完成时,用过去分词。 ·On receiving a phone call from his wife saying she had a fall, Mr. Gordon immediately rushed home from his office. 一听到他妻子打电 话说她摔了一跤,戈登先生马上离开办公室往家赶。 [江西] (表主动) 分考点 2 分词作定语 · We must keep a secret of the things being discussed here. 我们必须对在此讨论的问题保密。(表被动、进行) ·The players selected from the whole country are expected to bring us honor in this summer game. 我们期待着从全国各地挑选出来的运动 员能在今年夏季的赛事中给我们带来荣誉。 [ 湖南 ] (表被动、完成) Point 2 作定语的不及物动词的分词形式为:现在分词和过去分词。现在分词表示动作正在进行;过去分词只表示一个动作已完成,不表被动。 ·falling leaves 正在下落的叶子 ( 表正在进行 ) ·fallen leaves 落叶 ( 表完成 ) 分考点 2 分词作定语 Point 动名词作定语时常置于被修饰词之前,用于说明被修饰词的用途、功能或目的。 ·a walking stick 拐杖 ·a reading room 阅览室 · a sleeping car 卧铺车 分考点 3 动名词 作定语 考点 45 非谓语动词作宾语、主语和表语的用法 分考点 1 非谓语动词作宾语 分考点 2 非谓语动词作主语 分考点 3 非谓语动词作表语 Point 1 表示下列含义的动词一般只接不定式作宾语,请牢记下面的口诀: 分考点 1 非谓语动词作宾语 即: decide/determine, learn, want, expect/hope; refuse, manage, wish, pretend; offer, promise, choose, plan; agree, ask/beg, help 等后一般只接不定式作宾语。 此外, afford, strive, happen, wait, threaten 等也要用不定式作宾语。 决心学会想希望,拒绝设法愿假装。 主动答应选计划,同意请求帮一帮。 · The police officers decided to conduct a thorough and comprehensive review of the case. 警官们决定对这起案件进行一次周密而全面的审 查。 [ 2015 江苏] ·We managed to get to the airport in time. 我们设法及时赶到了机场。[ 《 牛津高阶 》 ] 分考点 1 非谓语动词作宾语 Point 2 表示下列含义的动词或动词短语后一般只接动名词作宾语,请牢记下面的口诀: 分考点 1 非谓语动词作宾语 考虑建议盼原谅,承认推迟没得想。 避免错过继续练,否认完成就欣赏。 禁止想象才冒险,不禁介意准逃亡。 即 : consider, suggest/advise, look forward to, excuse/pardon; admit, delay/put off, fancy( 想要 ); avoid, miss, keep/keep on, practice; deny, finish, enjoy/appreciate; forbid, imagine, risk; can’t help (禁不住) , mind, allow/permit, escape 等后一般只能接动名词作宾语。 此外, be used/accustomed to ( 习惯于 ), lead to, devote to, go back to, stick to, object to, get down to, pay attention to, can’t stand ( 忍受 ), give up, feel like, insist on, thank you for, apologize for, be busy (in), have difficulty/trouble ( in )等动词短语后也要用动名词作宾语。 分考点 1 非谓语动词作宾语 · David suggested selling your house and car to pay the debt. 戴维建议卖掉你的房子和车来抵债。 ·The law forbids smoking in public buildings. 法律禁止在公共场所吸烟。 ·Lydia doesn’t feel like studying abroad. Her parents are old. 莉迪亚不想出国读书,因为她的父母亲都老了。 [四川] 分考点 1 非谓语动词作宾语 Point 3 有些动词或动词短语既可接动词不定式作宾语 , 也可接动名词作宾语,但表示的含义不同。 分考点 1 非谓语动词作宾语 后接动词不定式或动名词作宾语意义不同的动词 ( 短语 ) ·I regret to tell you that I can’t come. 我很遗憾地告诉你我不能来。 · He bitterly regretted ever having mentioned it. 他非常懊悔提起那件事。 [ 《 牛津高阶 》 ] ·I remembered to lock the door before I left the office, but forgot to turn off the lights. 我记得离开办公室之前锁门,但忘了关灯。 [安徽] ·I remember meeting her at a party once. 我记得曾在某次聚会上见过她一面。 分考点 1 非谓语动词作宾语 Point 4 不定式作动词(短语) learn, decide, know, wonder, show, tell, understand, explain, teach, advise, find out 等的宾语时,通常用不定式短语,即“连接代词 / 副词( how, what, whether, where, when , who 等) + 不定式”。 ·—There’s no use having ideas only. —Don’t worry. Peter can show you how to turn an idea into an act. —— 光有想法是没有用的。 —— 不要担心,彼得会告诉你如何将想法转变为行动。 [ 辽宁 ] 分考点 1 非谓语动词作宾语 【 特别注意 】 此用法中的不定式的逻辑主语须与句子的主语或宾语保持一致,否则要用宾语从句。 ·I wonder how he solved the problem . 我想知道他是怎样解决这个问题的。 ·I don’t know whether the guest will come tonight . 我不知道那位客人今晚是否会来。 分考点 1 非谓语动词作宾语 Point 1 分考点 2 非谓语动词作主语 不定式作主语,一般表示具体某一次的动作。常用 it 作形式主语,而将真正的主语不定式放在句末,以使句子保持平衡。 · To climb the mountain is hard work but to go down the mountain is great fun. 上山很艰难,下山却很好玩。 ·No matter how bright a talker you are, there are times when it’s better to remain silent. 不论你是多么能说会道,有些时候保持沉默会更好。 [ 浙江 ] Point 2 动名词作主语常表示抽象的、泛指的概念;也可用 it 作形式主语,将真正的主语动名词放在句末。常用于固定句型 : It’s a waste of time doing… ; It’s no use/no good doing… ; It is useless/nice/interesting… doing… ; There is no doing… 。 · Knowing basic first-aid techniques will help you respond quickly to emergencies. 掌握基本的急救技能将会有助于你在遇到紧急情况时迅速 作出反应。 [ 福建 2013] 分考点 2 非谓语动词作主语 · It is no use complaining without taking action. 不采取行动而只是抱怨是没有用的。 ·There is no joking about such serious matters. 这样严肃的事开不得玩笑。 分考点 2 非谓语动词作主语 Point 1 不定式作表语常用来表示预定要发生的动作,也可用来表示未来的可能性和假设;但当不定式所作的表语仅用来说明主语的内容时,这时的不定式只作单纯的表语,而不具有未来的含义。 ·His wish is to be a doctor in the future. 他的愿望是将来当一名医生。 · My job is to clean the rooms every day. 我的工作是每天打扫房间。 分考点 3 非谓语动词作表语 Point 2 动名词作表语多指抽象的、概念性的动作,可以是多次的、经常性的行为。 ·Our job is playing all kinds of music. 我们的工作是演奏各种各样的音乐。 分考点 3 非谓语动词作表语 Point 3 get, become, look, seem, appear 等系动词后可跟过去分词作表语,表示被动或主语的状态。 ·This quotation from Winston Churchill tells us that we shouldn’t get discouraged right after failures. 温斯顿 · 丘吉尔的这句名言告诉我们,失败后我们决不能气馁。 [福建 2014 ] 分考点 3 非谓语动词作表语 【 特别注意 】remain 作“仍然是”讲时,后可接现在分词或过去分词作表语;作“仍需去做,有待处理”时,后接 to be done 作表语。 ·Please remain seated until all the lights are on. 请留在座位上,直到灯全都亮起。 [ 《 朗文当代 》 ] ·It remains to be seen whether the newly-formed committee’s policy can be put into practice. 新成立的委员会提出的政策能否实行还有待观察。 [陕西 2013 ] 分考点 3 非谓语动词作表语 考点 46 非谓语动词作补语的用法 分考点 1 不定式作补语 分考点 2 分词作补语 分考点 3 非谓语动词作感官动词、使役动词的宾补 Point 1 有些动词或动词短语后接不定式作宾补,即“动词 / 动词短语 + 宾语 + to do” 。常见的这类动词或动词短语有: 分考点 1 不定式作补语 · She patiently explained all the rules to the students and required everyone to follow them. 她耐心地向学生解释了所有的规则,并要求每个人都遵循这些规则。 [广东 2015 ] ·He depends on you to help him with his English. 他指望你帮助他学英语。 分考点 1 不定式作补语 Point 2 下列句型中常用不定式作主语补足语,它们是: sb. be said/ believed/known/reported/considered/thought + to do/to have done/to be done/to be doing/to have been done sth. ·He is said to have been cheated in the street. 据说,他在大街上被骗了。 ·The accident is reported to have killed two people. 据报道,那次事故中有两人丧生。 分考点 1 不定式作补语 Point 1 现在分词作宾语补足语时,句中的宾语往往就是其逻辑主语,该动词与宾语之间存在逻辑上的主动关系。 ·They use computers to keep the traffic running smoothly. 他们使用电脑以使交通畅通无阻。 ·Listen ! Do you hear someone calling for help? 听!你听到有人在呼救吗? 分考点 2 分词作补语 Point 2 过去分词作宾语补足语时,表被动、完成,该动词与宾语之间存在逻辑上的动宾关系。 ·Alexander tried to get his work recognized in the medical circles. 亚历山大努力使自己的工作在医学界得到认可。 [ 辽宁 ] ·The guests left most of the dishes untouched , because they didn’t taste delicious. 大部分的菜,客人们都没有动,因为它们不怎么好吃。 分考点 2 分词作补语 Point 1 感官动词 see, watch, observe, hear, notice 等的宾补有以下形式(以 see 为例): (1)see sb. do sth. 看见某人做了某事 (宾语与宾补为逻辑上的主动关系) ·I saw him leave a few minutes ago. 我看见他几分钟前离开了。 分考点 3 非谓语动词作感官动词、 使役动词的宾补 (2)see sb. doing sth. 看见某人正在做某事 (宾语与宾补为逻辑上的主动 关系) · As I got closer, I saw him kicking his legs in the air and breathing heavily. 当我走近时,我看见他的腿在空中乱踢,并且呼吸沉重。 [湖北 2015 ] 分考点 3 非谓语动词作感官动词、 使役动词的宾补 (3)see sb./sth. done 看见某人 / 某物被 …… (宾语与宾补之间为逻辑上的 被动关系) · I’d like to see the plan carried out . 我想看到这个计划被执行。 分考点 3 非谓语动词作感官动词、 使役动词的宾补 Point 2 常见的使役动词有四个: have, make, let, get ,表示“使,让”的含义。 (1)have/make/let sb. do sth. 以及 get sb. to do sth. 表示“让 / 使某人做某 事”,宾语与宾补为逻辑上的主动关系。 ·The teacher had/made/let some students stay in the classroom after school. =The teacher got some students to stay in the classroom after school. 放学后老师让一些学生呆在教室里。 分考点 3 非谓语动词作感官动词、 使役动词的宾补 【 特别注意 】make 用于被动语态时,其后要用带 to 的不定式作主语补足语。 ·He was made to work day and night. 他被迫日夜工作。 分考点 3 非谓语动词作感官动词、 使役动词的宾补 (2)have/get + sb./sth.+ doing sth. 表示“让某人一直做某事;让某物处于 某种状态”。 · He had the fire burning all the night. 他让火燃烧了一夜。 · She got her bike running very fast. 她把自行车骑得飞快。 分考点 3 非谓语动词作感官动词、 使役动词的宾补 【 特别注意 】 have sb. doing sth . 用于否定句中,常与 can’t, won’t 等连用,表示“不能容忍某人做某事”。 · I won’t have you speaking to your dad like that. 我不容许你和你父亲那样讲话。 (3)“have/get+ 宾语 +done” 有三重含义:表被动动作(主语可能参与了, 也可能没参与);让别人做某事(主语未参与动作);主语遭遇了某 事。 · Before driving into the city, you are required to get your car washed . 在开车进城之前,你需要找人洗洗车。[四川] · He had his wallet stolen on his way home. 在回家的路上,他的钱包被偷了。 分考点 3 非谓语动词作感官动词、 使役动词的宾补 考法 1 考查非谓语动词作状语的用法 考法 2 考查非谓语动词作定语的用法 考法 3 考查非谓语动词作宾语、补语、主语和 表语的用法 考法 1 考查非谓语动词作状语的用法 例 1 [课标全国 Ⅱ 2015·66 改编] 【 解析 】 分析句子结构并结合语境可知,此处应用不定式作结果状语, be adj . enough to do sth . 为固定结构,意为“足够 …… 去做某事”。故填 to cool 。 to cool 句意为:当新的一天到来时,墙壁已经释放完它们的热量,现在冷得足够能让房子在炎热的白天保持凉爽。 When a new day breaks, the walls have given up their heat and are now cold enough _____ (cool) the house during the hot day. 例 2 [天津 2014·5 改编] 【 解析 】 “only + 不定式”表示意想不到的结果。故填 to find 。 to find 句意为:她急切地从袋子里取出那条连衣裙试穿,结果发现它不合身。 Anxiously, she took the dress out of the package and tried it on, only _______ (find) it didn’t fit. 考法 2 考查非谓语动词作定语的用法 例 [课标全国I 2015·70 ] 【 解析 】 从句的谓语动词是 arranges ,所以此处应用非谓语动词; people 和 live 之间是主动关系,故填 living ,作后置定语修饰 people 。 living Abercrombie & Kent, a travel company in Hong Kong, says it regularly arranges quick getaways here for people ______ (live) in Shanghai and Hong Kong. 句意为:香港的一家旅游公司 Abercrombie & Kent 说,他们经常在这儿(阳朔)为居住在上海和香港的人安排方便的度假。 考法 3 考查非谓语动词作宾语、 补语、主语和表语的用法 ( 1 )作宾语 ①有些动词后一般只接不定式作宾语,如: decide, determine, learn, want( 想要 ), expect, hope, wish, refuse, manage, pretend, offer, plan, agree, ask 等。 ②有些动词或动词短语后一般只接动名词作宾语,如: consider, suggest, look forward to, avoid, put off, admit, delay, fancy, imagine, forbid, allow, mind, finish 等。 ③有些动词既可接不定式也可接动名词作宾语,但有时意义不同。 如: forget, remember, regret, mean 等。 考法 3 考查非谓语动词作宾语、 补语、主语和表语的用法 ( 2 )作补足语 ① 上面这类含有不定式或分词作宾语补足语的句子变为被动结构时,原来的宾语补足语便成为主语补足语。 考法 3 考查非谓语动词作宾语、 补语、主语和表语的用法 ②独立主格结构中非谓语动词的用法 考法 3 考查非谓语动词作宾语、 补语、主语和表语的用法 (3) 作主语和表语:一般情况下,表抽象的一般行为时多用动名词;表 某一具体动作,特别是某一将来的动作时多用动词不定式。 例 1 [课标全国 Ⅱ 2015·64 ] 【 解析 】 介词 without 后面用名词或动名词作宾语,故填 using 。 using 句意为:除了朴素之美外,令人赞叹的是这些土坯房具有不使用电气设备就能自动进行空气调节的能力。 In addition to their simple beauty, what makes the adobe dwellings admirable is their ability to “air condition” a house without _______ (use) electric equipment. 例 2 [陕西 2015·18 改编] 【 解析 】 宾语 his mother 与 take good care of 之间是被动关系,且表完成,故用过去分词作宾补。答案为 taken 。 taken 句意为:在非洲从事两年的医疗服务后,李医生回来看到母亲在家里受到很周到的照顾很高兴。 Back from his two-year medical service in Africa, Dr. Lee was very happy to see his mother ______ (take) good care of at home. 例 3 [江苏 2015·24 改编] 【 解析 】 分析句子成分可知逗号前是独立主格结构, time 和动词 spend 之间是被动关系,故填过去分词。该独立主格结构相当于一个原因状语从句,还原为从句即为 because much time is spent sitting at a desk 。答案为 spent 。 spent 句意为:由于上班族很多时间都坐在办公桌前,因此他们普遍受健康问题的困扰。 Much time _______ (spend) sitting at a desk, office workers are generally troubled by health problems. 易错知识 易混清单 易混 1 need/require/want/deserve 的用法 易混 2 worth , worthy, worthwhile 的用法 易混 1 need/require/want/deserve 的用法 need , require , want 作“需要”讲, deserve 作“应受,应得”讲时,其后接动名词的主动形式( doing )或不定式的被动形式( to be done ),表示“(某事)需被做”。 ·The road needs/wants/requires repairing/to be repaired . 这条道路需要修缮。 ·We’ve had a good start, but next, more work needs to be done to achieve the final success. 我们已经有了一个好的开始,但是为了取得 最后的成功,接下来会有更多的工作要做。 [湖南] be worth 后用动名词的主动形式( doing )表示被动意义,而 worthy 则需用被动形式。 易混 2 worth , worthy, worthwhile 的用法 易混 2 worth , worthy, worthwhile 的用法 · The book is well worth reading . =The book is worthy to be read . =The book is worthy of being read . 这本书值得好好读。查看更多